Table of content
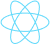
Key Emerging Technologies in Manufacturing in 2025
Industry 4.0, synonymous with smart manufacturing in the U.S. context, represents the fourth industrial revolution driven by the deep integration of digital technologies — such as AI, IoT, cloud computing, and advanced analytics — into manufacturing processes to create interconnected, data-driven factories that enable real-time decision-making, enhanced productivity, flexibility, and agility amid reshoring and supply chain resilience efforts.
In the U.S., it builds on the third industrial revolution’s automation by fusing physical and digital systems, with federal policies like the CHIPS and Science Act and Inflation Reduction Act accelerating adoption in semiconductors, EVs, and clean energy sectors to boost domestic competitiveness.
Throughout 2025, the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies significantly boosted the U.S. manufacturing sector’s contribution to global value creation, reaching $3.7 trillion for manufacturers and suppliers. Domestic investments — driven by policies such as the CHIPS and Science Act, accelerated semiconductor and advanced manufacturing growth by Q4 2025. Source: McKinsey & World Economic Forum, 2025 Analyses
- AI & Machine Learning are shifting from pilots to real deployment, delivering 15-25% cost reductions in supply-chain-intensive industries like semiconductors. (McKinsey Global Institute, 2025 Technology Trends).
- Digital Twins unify real-time data to run full-factory “what-if” simulations, cutting downtime up to 20% and accelerating reshoring. (Deloitte).
- Robotics handle dynamic, non-repetitive tasks to boost precision and scalability in automotive and electronics assembly. (McKinsey).
- Industrial IoT (IIoT) combined with edge, cloud, AI/ML, and robotics is projected to generate $1.2-3.7 trillion in annual economic value for manufacturing through real-time monitoring and resource optimization (McKinsey).
- Blockchain powers product provenance tracking and digital product passports for IoT devices, ensuring end-to-end supply-chain transparency and reducing fraud, with the manufacturing blockchain market reaching ~$30 billion. (Statista & Deloitte).
- Private 5G virtualizes PLCs to enable wireless real-time machine control, cutting deployment costs by orders of magnitude and lifting productivity by ~20%. (Ericsson & NAM).
- Edge Computing enables ultra-low-latency factory AI by processing data locally, reducing cloud reliance and creating up to $175B in value. (Gartner).
AI and ML
In 2025, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have become the cornerstone of manufacturing innovation, driving the evolution from Industry 4.0 to fully intelligent, resilient, and sustainable smart factories.
Key Trends:
- Predictive Maintenance. ML models analyze sensor data in real time to predict failures before they occur, shifting from reactive to proactive strategies that minimize disruptions. This integration with IoT enables dynamic adjustments, such as optimizing spare parts inventory based on failure probabilities.
- Generative AI & Digital Twins. GenAI creates optimized designs; digital twins simulate entire production scenarios, now enhanced by federated learning for privacy-preserving multi-plant collaboration. These twins generate synthetic data for rare failure scenarios, improving model robustness and enabling virtual testing that accelerates innovation cycles.
- Edge AI. AI inference runs directly on factory floor devices, reducing latency to under 10ms for instant process adjustments like anomaly detection in high-speed lines.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots) + AI. Cobots equipped with multimodal LLMs and reinforcement learning now work safely alongside humans, featuring intuitive interfaces and mobile platforms for flexible deployment. AI enhancements allow cobots to learn from human demonstrations, adapting to unstructured tasks like assembly in variable environments.
- Circular Manufacturing. ML optimizes the use of energy, water, and materials while minimizing waste, with GenAI simulating circular scenarios for zero-waste redesigns. By 2025, AI tracks Scope 3 emissions in real-time, enabling compliance with EU CSRD and reducing environmental impact through predictive resource allocation.
Industrial IoT
According to Gartner, the IIoT market has grown to $582 billion with a 15% CAGR since 2021 (Gartner: IoT devices forecast). The focus is on AI, edge computing, and 5G to reduce downtime by 30-50% and improve efficiency by 10-20%. These innovations are accelerating Industry 5.0, with 78% of companies investing over 20% of their budgets in smart manufacturing, highlighting the need for strong IT/OT convergence.
- Deep AI and ML integration for predictive maintenance: IIoT systems powered by AI forecast failures, cutting downtime by 50% and costs by 20%. 46% of companies have adopted IIoT for real-time monitoring (Deloitte).
- Edge computing with intelligent processing: 75% of data is processed at the edge to enable real-time decision-making and reduce latency. This drives a 10% efficiency boost, with 65% of IIoT edge solutions becoming industrially aligned (Gartner).
- 5G for ultra-low latency connectivity: Enables human-robot collaboration and AR/VR in manufacturing, driving a 15% increase in OEE. 42% of companies are leveraging 5G for IIoT (Deloitte).
- Stability and green manufacturing: IIoT enables real-time energy monitoring, reducing waste by 20-30%. There is a strong focus on sustainability powered by live data (Deloitte).
- Cloud-based platforms and cybersecurity: 57% of companies use cloud infrastructure for IIoT, secured with zero-trust protocols. Security is a top priority for building trustworthy IIoT systems (Gartner).
- Industrial metaverse and computer vision: AI-powered IIoT supports virtual testing environments, while computer vision boosts quality control accuracy by 25%. 95% of new IIoT deployments include AI-edge inference (Gartner).
Digital Twins
The Digital Twin market has grown to €16.5 billion with a CAGR of 39.8%, driven by a focus on AI, IoT, and sustainability.
Key Trends:
- AI-powered optimization: Digital twins with AI simulate production lines in real time, predict micro-downtime, and boost efficiency by 22-50%. Example: Siemens and Microsoft Azure for predictive maintenance in the automotive industry.
- 3D digital twins for simulation and R&D: Virtual replicas of factories and products enable testing of what-if scenarios and reduce physical prototypes by 40%. Used in agile design by Autodesk Fusion 360 and Pratiti Technologies in heavy industry.
- Integration with 3D printing and additive manufacturing: Digital twins optimize printing parameters, detect defects using AI/ML, and accelerate iterations in lightweight automotive components. AMFG reports a 30% waste reduction in prototyping.
- GPU-accelerated frameworks for real-time performance: Synopsys with NVIDIA Omniverse and Ansys Fluent enable dynamic line optimization (Krones AG: +15% productivity). Open framework supports scalable simulations.
- Live digital twins with IoT for Industry 5.0: Real-time monitoring powered by ML enables forward-looking predictions and reduces operational risks.
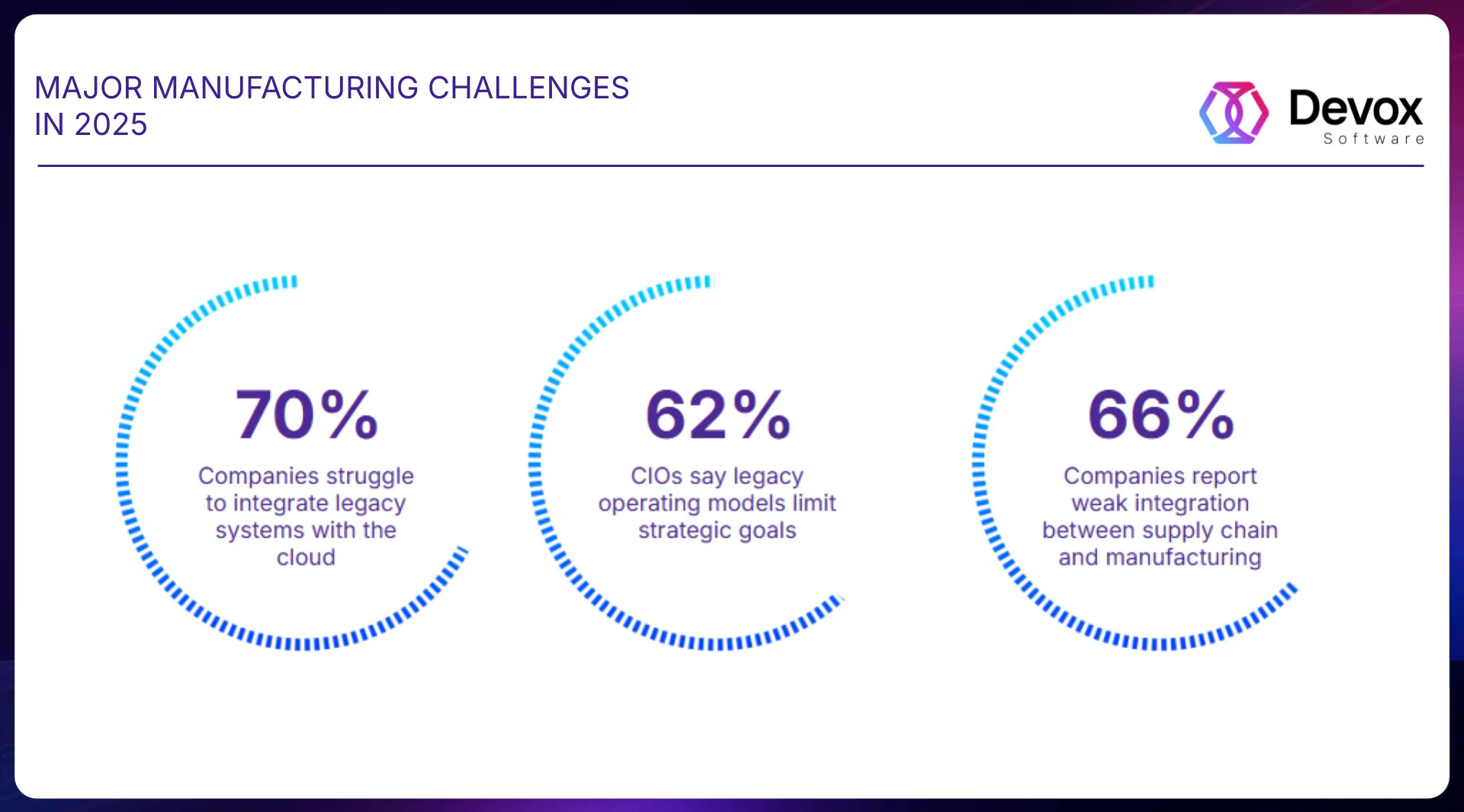
Major Manufacturing Challenges in 2025
Legacy Systems
Based on trusted 2025 sources (Gartner, McKinsey, Deloitte, IEEE), legacy systems remain a major challenge in manufacturing, hindering integration with IIoT, AI, and Industry 5.0. They create data silos, drive up maintenance costs (up to $300K annually for integration), and introduce security risks, slowing digital transformation by 20-30%. McKinsey reports that 70% of companies face issues integrating legacy infrastructure with cloud systems.
- Integration with Emerging Tech (GenAI, IIoT): Legacy infrastructure complicates AI and edge computing integration, causing data silos and delays in predictive maintenance. 62% of CIOs say their legacy operating models fail to support strategic goals (Gartner).
- High Costs and Inefficiency: Maintaining legacy systems costs over $300K annually in integration efforts, with outdated ERP systems cutting productivity by up to 20%. (McKinsey).
- Cybersecurity Risks: Legacy systems expose supply chains to security threats, especially with GenAI adoption — up to 75% of breach risks linked to IP leakage (Gartner).
- Interoperability and Data Silos: 56% of IT leaders cite legacy-to-OT/IT integration as a top challenge, limiting access to real-time data essential for smart factory operations (Deloitte).
- Disconnected Supply Chain and Manufacturing: 66% of respondents cite the lack of integration between supply chain and manufacturing as the top challenge for the next three years — slowing agile decision-making and investment coordination (Gartner).
- Data Integration and Silos: On average, companies use 897 applications, but only 29% are integrated — leading to persistent data silos and limiting data transformation for AI and analytics (Integrate).
Supply Chain Volatility
Based on reliable sources from 2025, supply chain volatility posed significant risks to manufacturing, driven by tariffs, geopolitics, and disruptions, leading to cost increases of 5-10% and productivity losses of 10-20%. Below are key challenges, each supported by one primary source.
Key Trends:
- Trade Uncertainty and Tariffs: 78% of manufacturers cited trade uncertainty as their top concern, with tariffs raising input costs by an average of 5.4% and prompting inventory front-loading, though negotiations (e.g., US-Mexico-Canada Agreement) offered limited relief (Deloitte).
- Resource Constraints and Supplier Reliability: 77% of leaders reported shortages in labor and budget for volatility management, with 52% facing quality issues from Tier 2+ suppliers, slowing ROI on dual sourcing efforts. Source: Forbes State of Manufacturing 2025 (Deloitte).
- Supplier Reliability: 77% of leaders reported shortages in labor and budget for volatility management, with 52% facing quality issues from Tier 2+ suppliers, slowing ROI on dual sourcing efforts. Source: Forbes State of Manufacturing 2025 (Gartner)
- Climate Disruptions: Floods and hurricanes (e.g., impacting quartz mines) caused shutdowns in semiconductors and automotive sectors, affecting 84% of firms and increasing energy price volatility by 9% via rail rerouting (Mckinsey)
- Trade Fragmentation: Geopolitical tensions (e.g., US-China conflicts, Red Sea attacks) disrupted semiconductor and EV scaling, with 90% of companies facing delays due to concentrated raw materials (70% controlled by single countries), necessitating reshoring/nearshoring. (Mckinsey)
Cybersecurity
Based on 2025 reports, cybersecurity threats in manufacturing have intensified due to the rise of smart factories, IIoT, and AI — with a sharp focus on supply chains and OT systems. 40% of manufacturers experienced 6-10 breaches, leading to 15-20% productivity losses and driving security investments beyond 20% of IT/OT budgets. Key challenges include:
- OT Vulnerabilities: 40% of manufacturers reported 6-10 cyberattacks in the past year, with over 1,200 known OT vulnerabilities across 300+ vendors. Increased connectivity in smart factories compounds risks and complicates remediation of quality issues. (Deloitte)
- Supply Chain Cybersecurity & IP Leakage: Supply chain security has reached the “Peak of Inflated Expectations,” with GenAI-related risks among trading partners leading to data breaches and intellectual property leakage. 81% of boards now see cybersecurity as a business risk, but 58% want stronger visibility into tech-related threats. (Gartner)
- Integrating GenAI into legacy systems is creating growing disillusionment, especially in planning and manufacturing workflows. Boards often overestimate organizational readiness — only 31% qualify as early adopters. This gap exposes cyber-physical vulnerabilities in Industry 4.0 environments, including targeted sabotage in advanced materials like composites. (HBR)
Scaling Innovation
Manufacturers are deploying AI, IIoT, edge and next-generation connectivity at a pace their organizations struggle to match. McKinsey’s 2025 analysis shows the same adoption pattern across industries: technology accelerates, while integration, workflows and decision cycles lag behind. The momentum of Industry 5.0 is real, yet scaling it requires IT/OT alignment, cleaner data foundations and operating models built for continuous change.
- AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance: AI can cut downtime by 50% and costs by 20%, yet 46% of real-time IIoT deployments struggle to keep data clean enough for reliable forecasting. (Deloitte).
- Edge Computing: With 75% of data processed at the edge and 65% of solutions becoming industrial-grade, teams face rising complexity in securing and updating distributed intelligence. (Gartner).
- 5G and Ultra-Low Latency: 5G lifts OEE by 15%, but 42% of adopters now depend on networks where even minor instability disrupts robotics and AR/VR workflows. (Deloitte).
- Sustainability: IIoT reduces waste by 20-30%, yet achieving consistent gains requires models that adapt to volatile loads and shifting environmental conditions. (Deloitte).
- Cloud Platforms and Cybersecurity: As 57% of manufacturers move IIoT to the cloud, the attack surface expands faster than zero-trust policies can contain. (Gartner).
- Computer Vision Virtual testing and computer vision improve accuracy by 25%, but 95% of AI-edge deployments must synchronize vast data streams without drifting from real-world behavior. (Gartner).
- Skills gap. In 2025, the biggest brake on smart manufacturing is talent: AI, robotics and IIoT scale across plants, yet hundreds of thousands of roles stay unfilled, slowing the productivity gains these technologies should unlock. (Mckinsey)
Forecasts and Expectations for 2026
Agentic Autonomy
By 2026, agentic AI will scale to 23% of manufacturers for fully autonomous production scheduling, cutting changeover costs by up to 20%. Agentic systems will dynamically reallocate capacity whenever throughput data indicates a better move.
Zero-Downtime Maintenance
AI predictive maintenance will reach >80% of smart factories by 2026, forecasting failures with 50% higher accuracy than today. Predictive engines will merge all reliability signals into one model that drives unplanned stops toward statistical noise.
Next-Gen Defect Elimination
Generative AI with GANs/VAEs will reduce manufacturing defects by 68% through next-generation computer vision systems. Generative inspection models will detect microscopic deviations well before reaching tolerance limits, preventing defects at the source.
Edge-First Revolution
Edge AI processors will hit $38 billion revenue in 2026, enabling real-time, low-latency energy optimization across factory floors. Edge processors will run sub-millisecond control loops that are impossible to achieve in the cloud, ensuring stability for high-speed lines.
Superhuman Cobots
AI-powered cobots will surpass human performance in assembly tasks, pushing the industrial robotics market to $15-20 billion. Cobots will modulate force, angle and speed via multimodal feedback to surpass human precision and repeatability.
Closed-Loop Battery
AI closed-loop control will become standard in battery manufacturing by 2026, slashing electrode-process downtime by 30%. Closed-loop control will constantly rewrite electrode parameters mid-run, eliminating variation once fixed manually.
25% Greener 2026
AI-driven biomimetics and circular models will cut manufacturing emissions 25% by 2026 under Industry 5.0 frameworks. Energy models will auto-optimize motors and heaters as conditions change, making sustainability an always-on control variable.
Domain LLM Takeover
Domain-specific LLMs will dominate niche manufacturing in 2026, blending centralized and edge AI for bespoke robotic productivity leaps. Domain LLMs will encode machine logic and failure patterns, becoming the reasoning engine for robotics and line-level decisions.
Strategic Innovation Roadmap in 2026
By 2026, manufacturers that lead in innovation treat workforce development as part of the same operating system as data, automation and AI. Cross-industry AI research from 2025 shows that technology scales only when skills, processes and governance evolve in parallel. The most advanced manufacturers now invest in talent pipelines and upskilling institutions with the same discipline they apply to capex and digital programmes.
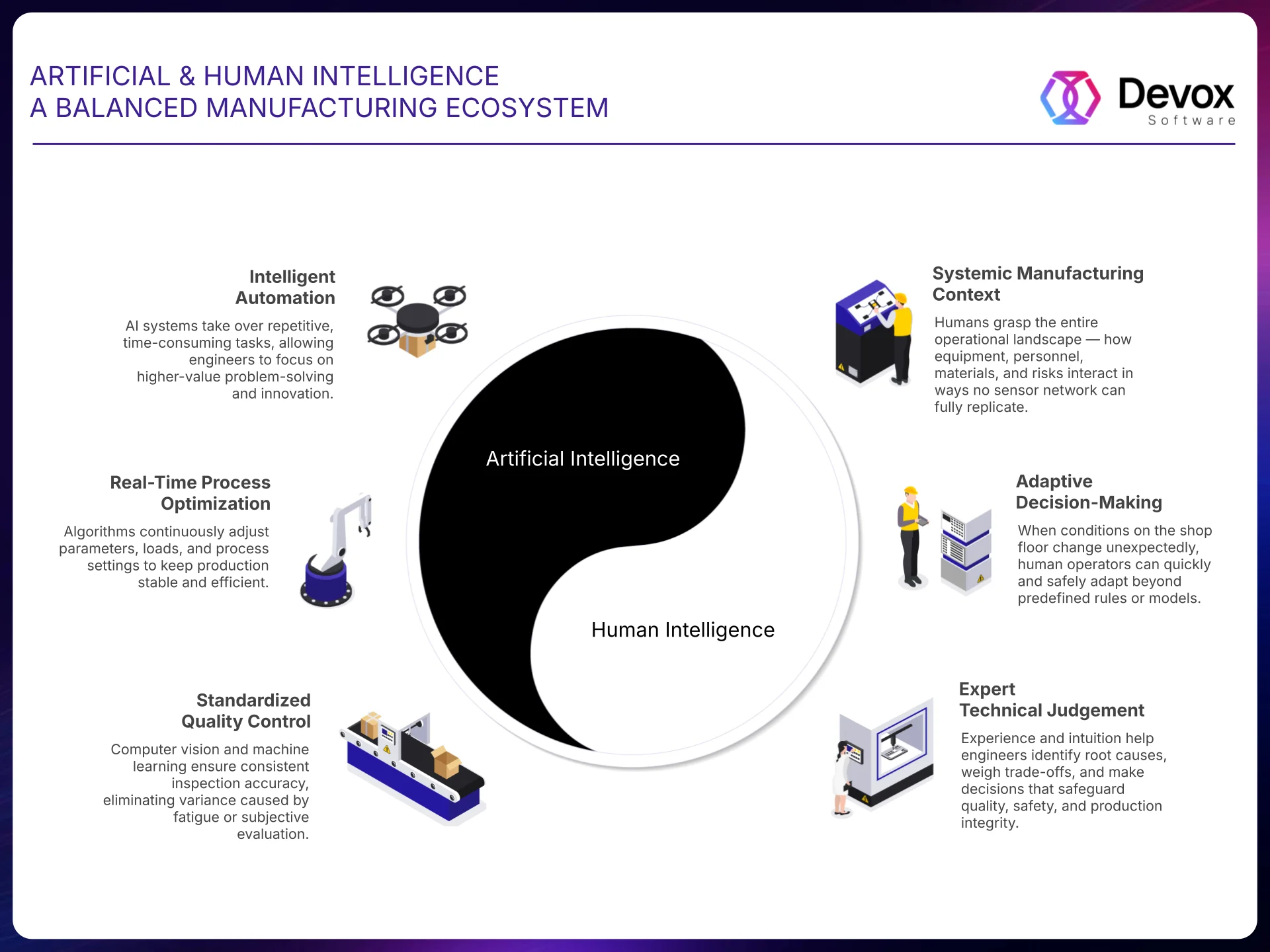
This synergy transforms every 2025 constraint into a strategic advantage in 2026. Legacy systems evolve into springboards for agentic AI. Cybersecurity transforms into proactive resilience. Supply-chain volatility becomes the training ground for adaptive intelligence.
The factories that will lead the coming decade are already building this harmony today. They equip machines with superhuman precision and speed, and they empower people with augmented insight, decisive authority, and creative freedom. When artificial and human intelligence complement each other seamlessly, manufacturing moves beyond efficiency and resilience — it becomes antifragile, innovative by design, and sustainably dominant.
The workforce dimension will define how quickly AI-driven manufacturing can scale. As the Manufacturing Institute highlighted in 2025, the sector still struggles with a perception problem: many potential workers picture factories as “dirty, dark and dangerous,” even as AI-enabled, sensorised and highly automated plants increasingly resemble clean, high-tech environments. Shifting this perception and expanding talent pipelines become essential prerequisites for Industry 5.0.
Strategy Road Map
This six-step roadmap outlines a clear path to modernization: establish an accurate system baseline, unify data for AI readiness, decouple logic from legacy architectures, scale AI into operations, reinforce governance for reliability, and embed continuous improvement into the operating model.
System Truthing
Establish a single, uncompromising system map that exposes both safe change zones and hidden production risks.
Data Unification
Unify all operational signals into one semantic backbone to eliminate fragmentation and make every site AI-ready.
Logic Liberation
Extract and modularize legacy logic to preserve current behavior while unlocking scalable automation and AI.
AI Operationalization
Embed AI directly into workflows so real-time signals translate into predictable, measurable performance gains.
Governance Hardening
Enforce discipline MLOps governance to keep all models versioned, traceable, reproducible, and safe at scale.
Continuous Evolution
Adopt a continuous modernization model that builds value across plants, products, and regions.