Table of content
How to Use AI for Predictive Maintenance in Industrial Systems
For the past few years, the Devox Software team has been focused on industrial enterprises, switching them from “run-to-failure” and time-based maintenance to an AI predictive maintenance service. We’ve witnessed how AI is turning from a flashy feature to a reliable business tool, driving tangible results.
What does AI for predictive maintenance in industrial systems even mean? Does it bring real value to the table? We’re not going to dupe our case studies here; instead, let’s consider practical techniques from our hands-on experience. Ready to start? Let’s cover the solution from A to Z.
What’s the Difference between Preventive and AI-Based Predictive Maintenance?
Before we talk about AI in predictive maintenance, it would be helpful to talk about three maintenance types that you’ve probably already implemented in your facility.
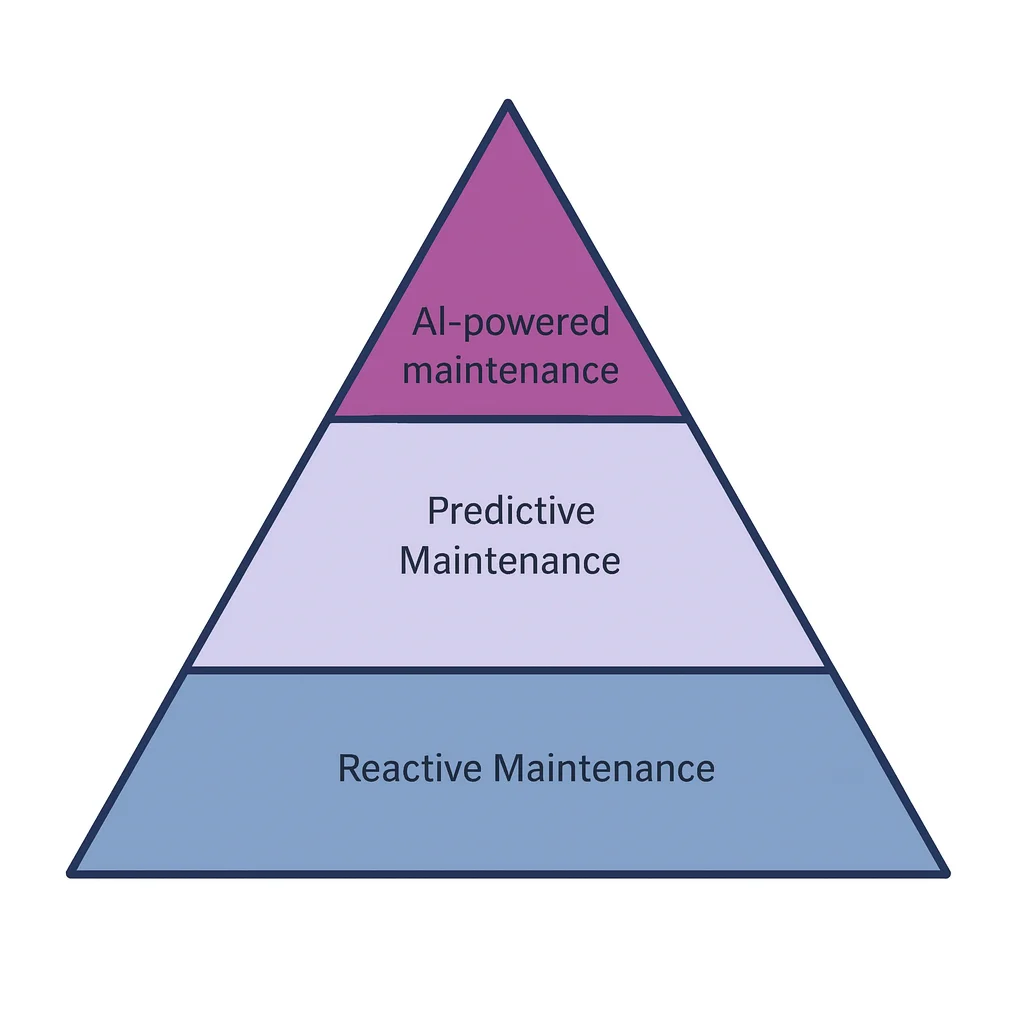
Reactive Maintenance
Reactive (in other words, a “run-to-failure” approach) means that you only fix things after they break. Despite the obvious simplicity and potential cost savings, this approach is completely unsuitable for large enterprises:
- You can’t predict failure-connected disruptions; therefore, plan the production,
- The cost of urgent repairs is higher,
- It’s difficult to find a correspondent expert in time,
- Safety and compliance concerns arise,
- Sudden failures may bring more severe damage to machinery and equipment, leading to more costly repairs.
To sum up, it’s easier to maintain machinery and equipment on schedule than to put out fires constantly. It’s like never going to the dentist until the pain is too much to handle. Worst-case scenario.
Preventive Maintenance
Another layer is called preventive maintenance, meaning you service equipment on a fixed schedule: every 3 months, every 1,000 hours, or every 10,000 cycles, depending on the technical recommendations. You may think that’s a brilliant idea, what could be better, but it has one major downside.
The plan is based on averages and general manufacturing recommendations, not on the real, current condition of each asset. Truly, it reduces chaos vs. pure “run-to-failure,” but you still over-maintain some machines and miss emerging problems on others. Here’s where AI predictive maintenance comes in.
AI-Based Predictive Maintenance
For predictive maintenance with AI, you unite various real-time sensor data (vibration, temperature, current, pressure, or images) with machine learning models to comprehend each metric and understand how each asset actually behaves.
Predictive maintenance using AI spots subtle anomalies and degradation patterns, estimates remaining useful life, and literally tells you, “This equipment needs service now, while these three are fine for another 500 hours.” As a result, your business moves from static schedules to just-in-time interventions, ultimately cutting unplanned downtime and unnecessary work.
What AI Really Brings to Predictive Maintenance
Traditional predictive maintenance stands on simple thresholds or statistical models. AI in predictive maintenance, however, differs in a few fundamental ways, widening the possibilities span:
-
- Data Depth: AI-based predictive maintenance operates on multivariate measurements from many systems, rather than a few criteria for each asset.
- Learning Patterns: MLM understands what is usual for each asset and finds little changes long before a rigid threshold would set off an alarm.
- Improving with Time: AI models improve as they experience more failures and close calls.
- Comprehensive Insights: Many modern AI predictive maintenance technologies incorporate natural-language layers. For example, instead of mere color tags, engineers observe descriptions like “bearing wear suspected on spindle 3; vibration pattern similar to incident #421 in March.”
In other words, AI and predictive maintenance are tightly connected to bring real value with clear priorities, unbiased analytics, and data-driven decisions.
How to Embed AI Predictive Maintenance, Manufacturing Version
We’ve prepared a battle-worn plan for implementing AI predictive maintenance, but we need to give you a word of caution. As with any other advancement, this needs investment and a skilled team to meet your needs. Devox Software is ahead of the curve with cutting-edge tech, so feel free to consult and follow this comprehensive step-by-step guide.
Step 1. Analyze Risks and Prioritize Assets
To begin, focus on several crucial assets, such as bottleneck machines in lines, bottleneck couplings, high-risk equipment, or problematic lines. Find the best failure modes and signals for each asset, covering the most value-driven gaps in security.
Step 2. Connect Sensors and Prepare Data
After addressing architecture, you need to prepare data for your active predictive maintenance AI. Some common sources include:
- Sensor Data: Vibration, temperature, current, oil, pressure, sound, and more,
- System Tags: For PLC and SCADA, MES events, and ERP work orders,
- IoT System and More: Data on quality and scrap, warehouse stocks, etc.
You need to unite these data streams together into an AI-powered IoT platform so that AI can see a clean, labeled dataset: normal periods, anomalies, and (preferably) labeled failures. There should be a clear connection between timestamps and events like alarms, stoppages, and maintenance operations. Additionally, all data must be resampled, denoised, and harmonized to produce an expected outcome.
Step 3. Choose an Architecture for Predictive Maintenance Edge AI
Consider adding edge AI, because sending everything to the cloud isn’t always possible or legal for many industrial processes. That’s where predictive maintenance edge AI might be useful. In particular, edge AI lets you run models directly on:
- Gateways are placed close to machines,
- Industrial PCs on the lines,
- Smart sensors or gadgets that are close to a PLC.
Recent research indicates that using AI models at the edge makes predictive maintenance systems faster and more reliable. It also protects data privacy and lowers bandwidth costs, so it’s the tech that you’d definitely consider implementing.
Step 4. Select the Right AI Model
Some common AI models for predictive maintenance include:
- Autoencoders and isolation forests for anomaly detection,
- RUL regression models for “how long until failure”,
- Models for classifying “which failure mode is most likely to happen next”.
Don’t overcomplicate things; add functions one by one. Begin with anomaly detection and a simple risk scoring for each asset. Once you have more records of reported failures, go on with the RUL regression.
Step 5. Put into Workflows
When AI predictive maintenance is separated from the processes, it doesn’t work well. Set up clear playbooks and add alerts to the tools your teams already use, such as CMMS, ticketing, and messaging. Add clear action plans to each possible situation, like:
- What happens when the risk score is higher than the threshold?
- Who gives the go-ahead for planned downtime to fix something before it breaks?
- How do the results get back into the model?
This is where a partnership with a reliable vendor comes in handy: outside data scientists and MLOps engineers with the highest field expertise develop the AI backbone, while your engineers make all the decisions and keep control of the domain logic.
How to Assess ROI for AI Predictive Maintenance?
Several separate research studies receive comparable figures. They claim that predictive maintenance reduces maintenance expenditures by 10-40%, unplanned downtime by 50%, and makes assets last about 20% longer. Also, AI predictive maintenance solutions cut maintenance costs by up to 25% and give a return on investment within 12 to 18 months.
But does it work for your business? Here’s a short example of a realistic manufacturing ROI. Let’s consider a plant with 8 packaging lines and calculate the impact of each hour of unscheduled downtime.
The starting cost of unplanned downtime is 10 events × 3 hours × USD 20,000 = USD 600,000. If we reduce breakdowns by 40% and lessen the time they affect by about 25%, the potential losses will be calculated as follows: 6 events lasting 2.25 hours × USD 20,000 = USD 270,000 a year.
The results will include not only the direct savings on downtime, reaching about USD 330,000 a year, but also help indirectly:
- Less overtime and parts for emergencies,
- Higher quality,
- Longer life for parts.
As a result, it proves that the effect of AI predictive maintenance beats the initial investments. So if your lines run in tough or isolated places like railroads, mines, electricity, or pipelines, predictive maintenance edge AI is frequently the only method to acquire accurate, quick information.
The Best Applications of AI for Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
We’ve gathered the use cases of how AI-based predictive maintenance works in real life. Here are the most common and valuable improvements.
Production Lines and Facilities
The first thing we want to mention is that AI helps manufacturing with quality checks and predicting maintenance costs. The same vision/IoT data that finds surface flaws can also show drifts that happen before machines break down. It’s applicable for robots, cutting tools, bearings, conveyors, packing equipment, and more.
Moreover, even taken generally, chillers, HVAC units, and elevators produce a lot of time-series data. AI uses that data to predict failures and use less energy.
Utilities and Power
Predictive maintenance AI monitors transformers, breakers, and rotating equipment to make assets last longer. The ML models process data from PD, partial discharge, and thermal imaging to identify problematic parts preemptively.
For instance, an AI predictive maintenance service pipes find leaks and corrosion by looking at pressure, flow, and sound patterns. As a result, the inspections pass faster and smoothly, and the overall safety situation improves.
Transportation
AI predictive maintenance in fleet maintenance results in 12–18% lower maintenance costs and 15–20% shorter unexpected downtime, for instance, for aircraft, making the fleet more available.
Simply put, AI tells you “when and why,” and your maintenance staff tells you “how.”
The End (Almost)
AI for predictive maintenance gives you fewer unplanned breaks, energy and cost savings, and longer life for assets, while granting better safety on the go. It enables quick, local decisions at the machine level while still having access to fleet-wide data in the background.
At Devox Software, we assist plants and other manufacturing facilities with AI predictive maintenance systems using the best practices and AI-powered tools like AI Solution Accelerator™. Let’s discuss if you want to find out where AI predictive maintenance gives you the best ROI in your setup.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is predictive maintenance edge AI?
Predictive maintenance leverages AI for you to execute your maintenance AI models on devices close to the machines (such as gateways, industrial PCs, and smart sensors) as well as on the cloud.
They look at sensor data in real time on the spot, identify problems, provide alarms right away, and just send summaries upstream. This means faster responses, less bandwidth, and better data privacy.
-
Is AI predictive maintenance only for big businesses?
No. Large companies were the first to deploy AI predictive maintenance service, but now small and medium-sized businesses use lighter versions of these services, SaaS platforms, and pre-built edge AI kits that don’t need significant data science teams.
-
How much information do I need to get the AI predictive maintenance project started?
For one asset family, start with a few months of sensor and event data. You can start with unsupervised anomaly detection and get better as you find more tagged failures.
-
What are some common problems with AI in predictive maintenance projects?
Most failures are due to problems with the organization, not the technology. For example, there is no clear owner, the technology isn’t integrated into CMMS or workflows, or people have unreasonable expectations.